Servers Monitoring
Using Gazer, you can monitor communication with computers, servers or other network devices.
You can determine the availability of devices using ping requests, TCP test connections, or higher level connections such as: making database queries, receiving a JSON document using the HTTP / HTTPS protocol, etc.
For this purpose, the following units may be useful to you:
For example, you have 3 PostgreeSQL database servers. The first level of monitoring is to check the availability of the host itself using Ping. It will provide information about the availability of the system over the network. The second level of monitoring is to check if it can connect to TCP port 5432, which is typically used by the PostgreeSQL server. This will provide you with information about the availability of the database server over the network. Finally, you can run a test SQL query from time to time. This will show that the database server is actually working and can accept requests from clients.
Some caution is important. Monitoring a server using a Ping unit is quite a harmless operation. But constant frequent connections to the server can negatively affect its performance. It is assumed that the interval between connection attempts will be about 10 seconds. This will not create additional load on the server and is usually sufficient to investigate the causes of the emergency. As for test queries, it is better to create a separate role in the database with very limited rights for this purpose. This will help limit the damage in the event of a credential leak or a dangerous test request.
After configuring the above three units:
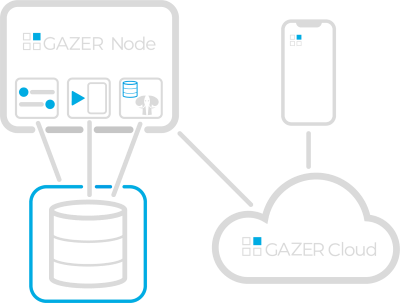
You will receive constant monitoring of your database servers. All indicators can be displayed on charts. Current readings can be published on a public channel. If you connect GazerNode to the cloud, access to information is possible from anywhere on the planet.
